PATIENT INFORMATION: DATA IMPLANTS (chip implants)
(chip implants, microchip implants, data implant, transponder, transmitting implants)
WHAT FOR ?
Data implants contain electronic data carriers that can store data, but also additionally receive and/or transmit data. Only implants that store or transmit data are discussed here.
Implants with special, active functions – such as stimulating implants at the heart (pacemakers, defibrillators) or at nerve tracts – are to be found in the relevant anatomical regions.
General use
Transmitting implants can be used for the following non-medical functions:
- identification (e.g., personal control, contact information, smartphone, device sharing
- key replacement, ticket replacement)
- access control (buildings, vehicles, companies, devices…)
- payment function
- handover of data
- being found
Medical use
In the healthcare sector, the following functions for transferring medical patient data are possible or conceivable (as they have not yet been implemented):
- medical data storage (e.g. blood group, vaccinations, allergies, diagnoses, medications)
- blood sugar control (diabetes implant chip)
- blood pressure control
- ECG control
- emergency call
Advantages
- Check in without password transfer
- No loss possible
- Does not contain private information like a wallet (name, surname, address, photo, authorization cards, bank details, signature…if wished)
- Location resistant (no GPS) and is not recognized by the airport because of the small amount of metal
FUNCTION
Data implants are used exclusively for data storage, recording and transmission.
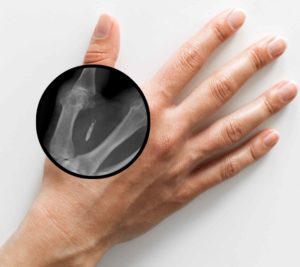
A preferred location for chip implant placement is between the thumb and index finger.
INDICATION
In the medical field, the indication and medical advice can be seen when a constant function control (e.g. blood glucose level) is useful. The application only for prophylactic purposes without the presence of a disease is subject to individual decision.
In the non-medical field, practical advantages can be the reason for a transmitting implant based on a subjective decision.
TIMES
Implants can usually be inserted with a cannula (similar to a syringe) in about 1-2 minutes. There is no functional limitation, possibly minor wound pain or swelling.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Specific contraindications are not known.
RISKS
The implants are inserted subdermally, i.e. just under the skin. This is risk-free, provided that the usual hygienic and anatomical rules are observed. Risks may exist in the case of certain diseases, e.g. blood disorders.
Allergic reactions are thinkable in case of an allergic disposition. Allergies to glass – the casing of the implant – are not known.
In the event of mechanical impact, e.g. in an accident, the implant capsule may break. If the shell breaks, metallic and plastic fragments come into contact with the body, which can lead to allergic reactions, and possibly also to injuries.
The fragments must then be removed. If there is a foreseeable risk of force being exerted on the implanted anatomical area during some activities or sports, it should be protected accordingly (e.g. by wearing gloves).
Commercially available magnets do not affect the implant. According to many experience reports, the CT and MRI are not dangerous.
Data protection
If a data transmission function is present, it cannot be excluded in principle that data can be stolen/read out (“stolen identity”).
Chips without an energy source should not be able to be detected (i.e., tracked externally). This may be the case for chips with an energy source and proprietary transmission functions.
On controls, the material of an NFC implant goes unnoticed. The metal content is too small to be detected by detectors.
FAILURES
Data implants are generally used in anatomically unproblematic body regions. Injury to vessels or nerves cannot be completely ruled out in the event of improper use.
A data implant can be easily removed. To do this, the site is anesthetized with an ointment or spray and a small incision is made. In this way, the NFC implant can then be pushed out again.
MATERIALS
The shell of the implant comes into contact with the body. This is usually made of glass. Glass is considered inert, and allergies are not known.
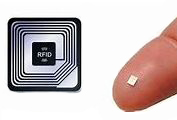
RFID chip
An RFID chip is a data carrier that can be identified and localized automatically and without contact via radio waves using RFID technology. RFID stands for Radio Frequency Identification. The chip contains a so-called transponder, which consists of an antenna and a circuit. This can receive and send electromagnetic signals. A permanent memory is also integrated.
NFC communication
NFC stands for Near Field Communication. It is based on RFID technology according to an international transmission standard for the contactless exchange of data by electromagnetic induction over short distances of a few centimeters and a data transmission rate of max. 424 kBit/s.
FIGURES / STATISTICS
Germany 2020: 3,500 persons
Sweden 2019: 5,000 persons
USA: n/a
In 2004, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved microchip implants from Applied Digital Systems to store medical information. In 2018, the FDA approved the use of medical implanted tags that allow continuous monitoring of blood glucose levels in diabetic patients.
SELECTED INFORMATION
n/a
LITERATURE
n/a
REGISTER
There is no known registry for chip implants.
The implant registry offers an online registration (fee 15.00€ + VAT) and you can print a personal implant passport for free.
| Disclaimer The information and links and whatsoever shown on this page are compiled with care. However, Implant-Register can´t take any responsibility for the information given, nor their content, nor their up-to-date nature, particularly in interlinked pages. You may help us with your contribution, granting us the decision to publish or not. Be careful with conclusions for yourself, in doubt double-check and consider medical solutions are individual and have to be found with an educated medical person. |