How does a breast implantation work
The preparation:
|
| Before implantation, a detailed examination is performed to determine which treatment is appropriate. Once the treatment option(s) has been found, a discussion is held with the patient to explain the type of treatment and the process. Before the actual treatment, the patient must give consent.
Sometimes pre-treatment may be performed.If palpation is suspicious and in any case in patients over 30 years of age, an X-ray examination is recommended beforehand. With the help of expander implants, a breast can be built up within up to four months by increasing the volume week by week. This is particularly useful in cases of low breast volume or after breast cancer surgery. |
Anesthesia |
| As usually, breast augmentation surgery takes one to two hours and takes place under general anesthesia. Local anesthesia with the addition of sedatives is also possible in principle. The advantage: the inpatient stay is shorter. |
The surgery |
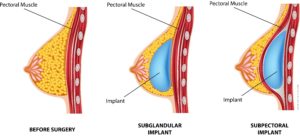
There are several ways of access to place a breast implant.
There are several sites where the implant can be placed. Both subglandular and subpectoral implant positioning are acceptable for every type of implant, however, depending on the individual anatomy, lifestyle, preferences, and the particular implant chosen, one position may be preferred over the other. Advantages of subglandular placement include no interference with pectoralis muscle function, no “animation,” or movement of the breasts that occurs with arm movement if the implant is subpectoral, and no requirement for stretching of muscle for the implant to settle into its final position. Women who compete athletically or who are very active with their upper body may want to avoid surgical manipulation of their pectoralis and dynamic breasts that are inevitabilities of sub-muscular (dual-plane) implant placement. Deeper implant placement helps more camouflage implant-related imperfections. So submuscular positioning is recommended for thin women with saline or cohesive silicone gel implants. Because the muscle better conceals implant characteristics, edges and rippling may be less visible. When a breast lift is simultaneously performed, submuscular implant placement improves blood supply to the overlying breast. The implant pocket under the pectoral muscle provides better opportunities for mammography. Disadvantage of implantation under the pectoral muscle: the multiple incisions of the pectoral muscle, as this method this method, may limit arm mobility. In any case, because of these and maybe some more individual variables, the surgeon must develop the breast implant pocket(s) extremely carefully and individually. |
| In some cases, more complex measures are performed, e.g. nipple relocation, breast lift. |
After the procedure |
As with any surgery, wound healing problems and secondary bleeding may occur. 7 – 10 days after surgery, the stitches can be removed – unless self-dissolving suture material was used. If a bacterial infection develops, a second procedure is necessary to remove the implants. New implants can be inserted after six months at the soonest. After about three months, the final aesthetic result can be checked. |
After completion |
| Implants require lifelong care. It is reasonable to have a control once a year, but the frequency should be decided individually by your surgeon. |
| A specific complication of breast augmentation is a hardening capsule formation (capsular fibrosis), which requires further surgery in about 20 percent and in about five percent of cases that occur, removal of the breast implant.
Breast augmentation with implants in any case entails further operations. At some point, the implant must be replaced because the material “fatigues”. Silicone gel implants are expected to last about ten to 15 years, saline implants somewhat less. |
 |
| This is the description of typical proceedings. Medical treatments are individual and your doctor may recommend different ones. |
| • |
| Disclaimer The information and links and whatsoever shown on this page are compiled with care. However, Implant-Register can´t take any responsibility for the information given, nor their content, nor their up-to-date nature, particularly in interlinked pages. You may help us with your contribution, granting us the decision to publish or not. Be careful with conclusions for yourself, in doubt double-check and consider medical solutions are individual and have to be found with an educated medical person. |